“We have essentially no patents in SpaceX. Our primary long-term competition is in China. If we published patents, it would be farcical, because the Chinese would just use them as a recipe book.”
Elon Musk
“We have essentially no patents in SpaceX”, said Elon Musk in his an interview in 2017 which gave hints on SpaceX strategy to use the trade secret route to protect its core technology.
So if not the core technology, what type of inventions SpaceX is protecting through patents?
SpaceX portfolio has 72 patents that belong to 26 patent families. Most of SpaceX patents are focused on its Starlink Project which aims to beam broadband internet connectivity from Space. The company has permission to put 12000 Starlink satellites in Earth’s orbit and so far it has put 600 satellites into orbit.
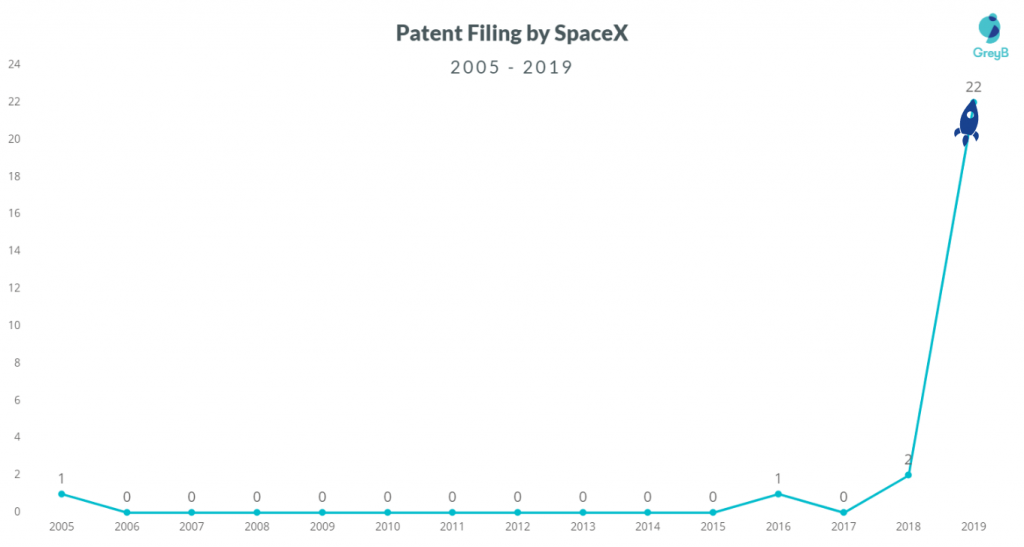
Patent Filing Trend of SpaceX Patents
The exhibit below represent the patent filing timeline of SpaceX patents.
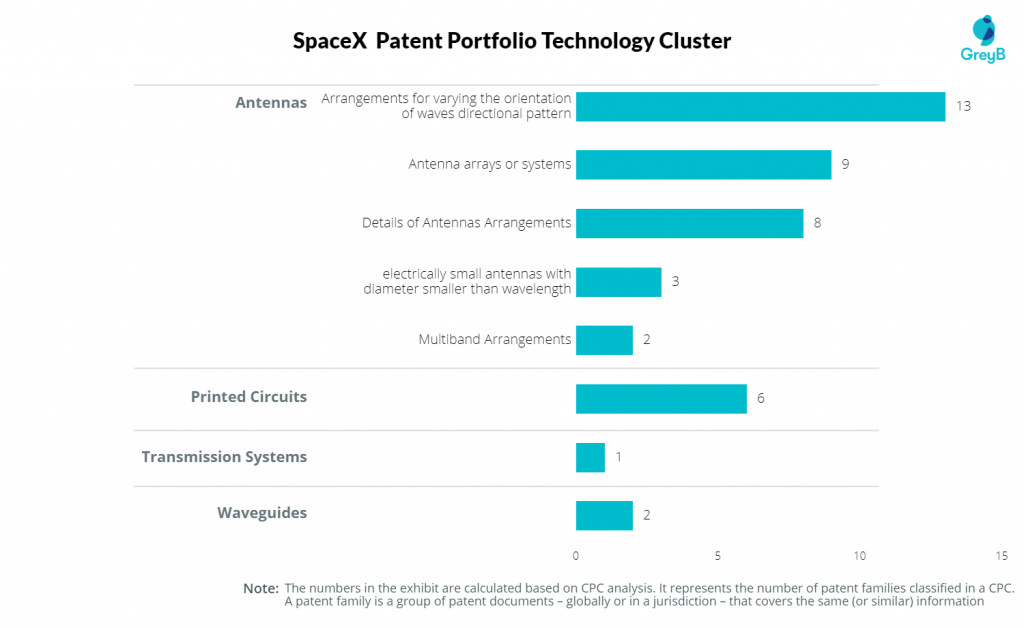
Technological Profile of SpaceX Patent Portfolio
To find the technological features, we categorized SpaceX patents based on CPC analysis. The number in exhibits below represents the number of patent families classified in a CPC. A patent family is a group of patent documents – globally or in a jurisdiction – that covers the same (or similar) information.
The patent portfolio of SpaceX has 72 patents that belong to 26 patent families categorized under 44 CPCs. We analyzed these CPCs to understand the technological profile of SpaceX’s patent portfolio. To let you know, more often a single patent gets classified into more than 10 CPCs which is the cause of the number of patent families categorized under different technology clusters exceeding the number of patent families which is 26.
The exhibit below represents the technological clusters of SpaceX’s patents. About 79.5% of SpaceX’s patents are focused on Starlink Antennas, 13.6% on printed circuits, and the rest on Transmission Systems, and Waveguides.
Thus, so far SpaceX is not filing patents for its core technology.
Want to know how the patent portfolio of Musk’s other company is like? Check it here: Patent Portfolio Analysis of Tesla
From https://www.tesmanian.com/blogs/tesmanian-blog/starlink-patent

SpaceX aims to provide low-latency, high-speed broadband internet globally, the aerospace company is building a constellation of internet-beaming Starlink satellites in low Earth orbit. SpaceX launches 60 satellites atop Falcon 9 rockets twice per month. To date, SpaceX has deployed roughly 960 satellites out of over 4,400 it plans to launch. The company rolled out a beta service of the network for select customers living in the northern United States and southern Canada a couple of months ago. To receive service from the satellites in space users mount a phased-array antenna dish the company nicknamed “Dishy McFlatface,” and connect to it via a Wi-Fi router device. SpaceX states that the Starlink dish features technology more advanced than what is currently on fighter jets. Today, December 3, the United States Patent & Trademark Office published a collection of SpaceX Starlink patent documents. The elaborated files were originally submitted to the patent agency in June 2020. Each document showcase graphics explaining how the satellite network works alongside the phased-array dish antenna. The eight patent documents linked below discuss in great detail the technology and hardware the Starlink dish antenna apparatus features:
- LASER-PERFORATED METAL HONEYCOMB MATERIAL “A perforated metal honeycomb structure is described. The perforated metal honeycomb structure may include a metal honeycomb structure having a plurality of laser-drilled holes wherein at least some of the plurality of holes are non-uniform in second, shape, and/or spacing between holes. In another embodiment, the perforated metal honeycomb structure may include an array of intercellular holes between hexagonal cells in the honeycomb structure. The array of intercellular holes may include at least a first hole and a second wherein the first and second holes are different from each other,” SpaceX wrote in the first Starlink patent published on March 19, 2020.
- ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING ANTENNA SPACER “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, an antenna assembly includes a patch antenna array including an upper patch antenna layer, a lower patch antenna layer, and a spacer therebetween, wherein the spacer includes a plurality of apertures defined by cell walls, wherein the each aperture aligns with an upper patch antenna element and a lower patent antenna element from the patch antenna array,” SpaceX wrote in the introduction of a newly published patent document titled “ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING ANTENNA SPACER,” which was filed June 2020, and published by the agency today with the documents below.
- ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING ADHESIVE COUPLING “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, an antenna assembly includes a plurality of layers defining an antenna assembly including a plurality of PCB layers and a plurality of non-PCB layers, the antenna assembly having a top surface and a bottom surface, and adhesive coupling between the PCB layers and the non-PCB layers,” SpaceX wrote in another document.
- ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING CHASSIS PORTION “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, a housing for an antenna system having a plurality of antenna elements defining an antenna aperture includes a chassis portion having an internal support portion for internal components for the plurality of antenna elements including a bonding portion for bonding an antenna stack assembly to the chassis portion, and a radome portion configured for coupling to the chassis portion to define an inner chassis chamber.”
- ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING FASTENER SYSTEM “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, a housing assembly for an antenna apparatus includes a radome portion, a lower enclosure portion, and a fastener system configured for coupling the radome portion and the lower enclosure portion couplable to form an inner compartment for antenna components of an antenna assembly.”
- ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING RADOME SPACING “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, a housing for an antenna system having a plurality of antenna elements defining an antenna aperture includes a chassis portion, and a radome portion configured for coupling to the chassis portion to define an inner chassis chamber, the radome portion having a planar top surface, wherein the radome portion is configured to have equal spacing between the planar top surface and a top surface of each of the plurality of antenna elements defining the antenna aperture.”
- ANTENNA APPARATUS HAVING HEAT DISSIPATION FEATURES “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, an antenna apparatus includes a housing assembly including a radome portion and a lower enclosure portion, wherein the radome portion and lower enclosure portion are couplable to form an inner compartment for housing antenna components of the antenna assembly, an antenna stack assembly disposed within the inner compartment, wherein the antenna stack assembly generates heat when in operation, and a heat transfer system within the inner compartment configured to facilitate the flow of heat toward the radome portion.”
- TILTED EARTH-BASED ANTENNA SYSTEMS AND METHODS OF TILTING FOR COMMUNICATION WITH A SATELLITE SYSTEM “In one embodiment of the present disclosure, a satellite communication system includes a satellite constellation including a plurality of satellites in non-geosynchronous orbit (non-GEO), wherein at least some of the plurality of satellites travel in a first orbital path at a first inclination, and an end point terminal having an earth-based geographic location, the end point terminal having an antenna system defining a field of regard for communicating with the satellite constellation, wherein the field of regard is a limited field of regard, wherein the field of regard is tilted from a non-tilted position to a tilted position, and wherein the tilt angle of the tilted position is a function of the latitude of the geographic location,” the filing’s introduction reads.